Service and Consultancy Structural Equation Modeling
Structural Equation Models (SEM) (Bollen 1989; Kaplan 2000) include a variety of statistical methods aimed to estimate plenty of causal relations, defined in the line of thought with a specific theoretical model, linking numerously latent complex concepts, each measured through its indicators (latent variables). The basic idea is that complexity in the data can be structured by taking into account causality relations among latent variables each measured by number observed indicators usually defined as observed indicators. It is in this sense that Structural Equation Models represent a statistical mix between Path Analysis (Tukey 1964; Alwin and Hauser 1975) and Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) (Thurstone 1931).
This statistical method is preferred by the researcher because it intend to estimates the multiple and interrelated relationships in a single and comprehensive model. Today, in the area of this analysis approach, we can build models in a covariance-based manner or partial least squares. What you can choose in the context of the service and consultancy structural equation modeling in Metodolog.pl?
Service and consultancy structural equation modeling. The primary step is a choice between PLS SEM Vs CB SEM.
Modeling of structural equations – choosing between PLS SEM and CB SEM is an extremely important decision. The popularity of modeling is increasing in academic research in many disciplines and is considered one of the most important statistical achievements in social sciences. Undoubtedly, modeling of structural equations presents several characteristics that attract researchers. This is due to the fact that individual research questions can be analyzed in a single, systematic and comprehensive statistical analysis model by generating relationships between many independent and dependent latent constructs at the same time. What’s more, the analysis itself not only assesses the structural model, but also the measurement model. This combination of analyzes allows you to measure the errors of observable variables as an integral part of the model, which makes the estimates provided by SEM better than those provided by classical regression analysis. Researchers using SEM can choose between CB-SEM (covariance based) or a variance approach known as PLS-SEM (partial least squares).
Use PLS SEM when:
The goal is to anticipate key constructs or identify them
the structural model is complex (many constructs and many indicators)
The observation sample is small and/or the data is not compatible with the normal distribution
The plan is to use the results of the latent variable in subsequent analyzes
Use the CB-SEM method when:
The goal is to test the theory, confirm the theory or compare alternative theories
Errors require an additional specification, such as covariance (the distincive feature of these two methods)
The structural model has circular relationships (bi-directional feedback loops)
The test requires a comprehensive assessment according to the matching criteria
What we can do for you?
Our service and consultancy in structural equation modeling help you with choosing appropriate SEM approach with followed topics:
We can help you with defining latent constructs
We can help you with choosing a suitable research design of the study to gather empirical data
We can help you with the developing appropriate measurement model and indicators
We can help you with assessing the measurement model accuracy and validity
We can help you with assessing matching data to the structural model
We can help you with examine the structural model validity
… and many more advanced topics in the area of the service and consultancy in structural equation modeling and related areas.
If you want to take advantage of our service and consultancy in structural equation modeling,
You can call us +48 798 30 95 31 (Konrad Hryniewicz) or send a mail metodolog.pl@gmail.com
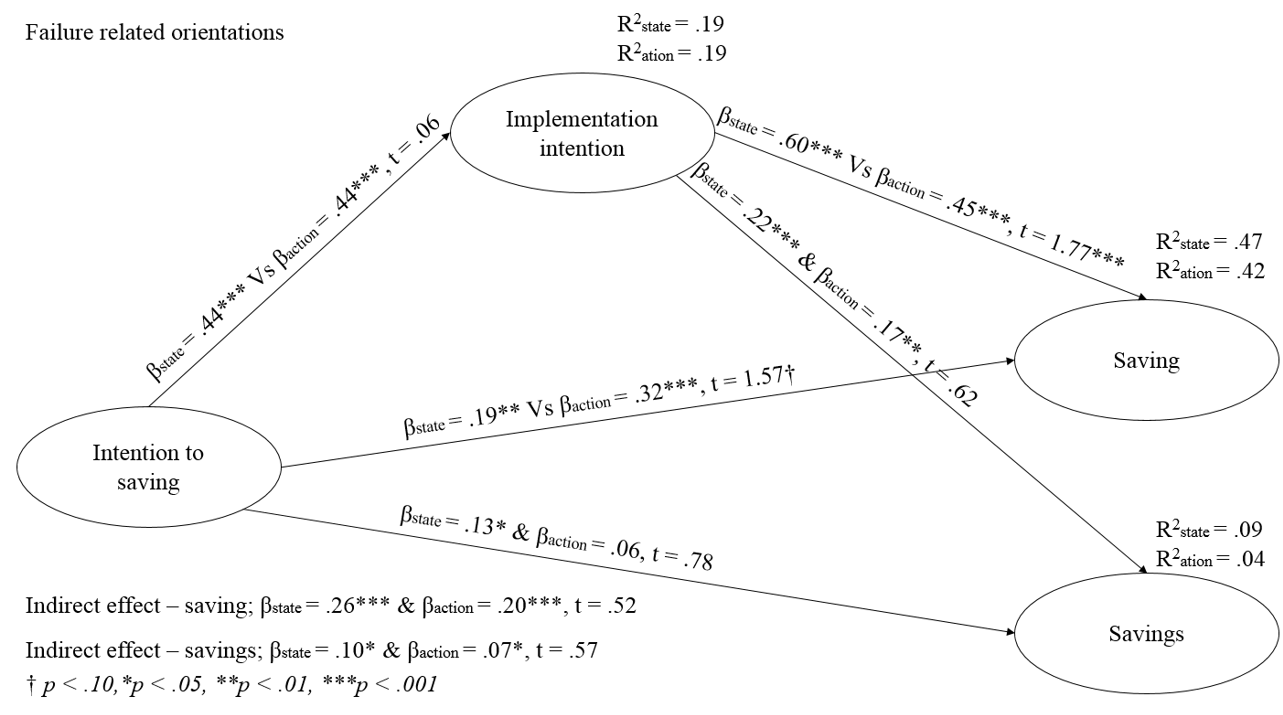
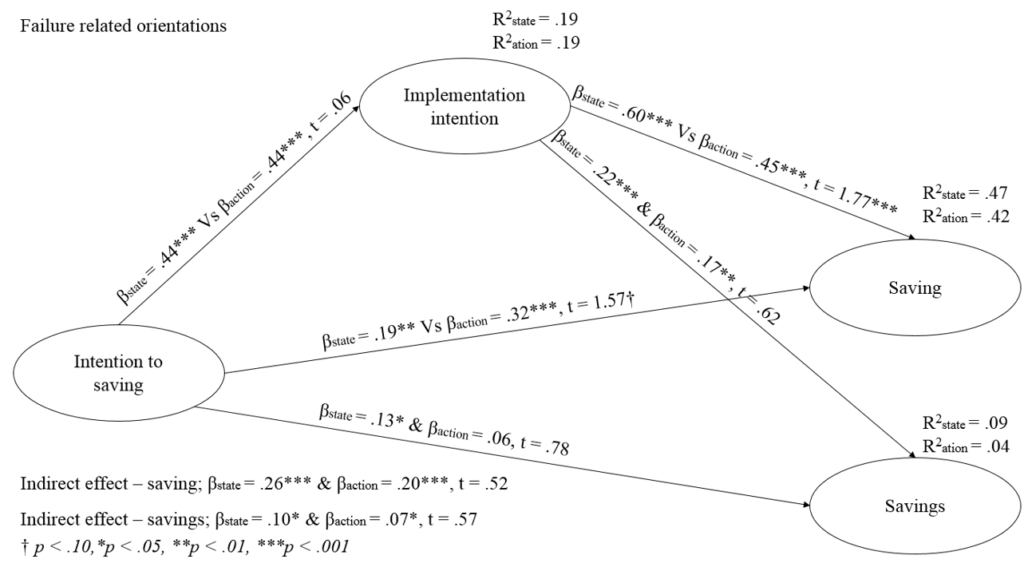
An example of the structural equation model in the study about will and cognition in course of action in the savings area. Estimates of the moderation mediation effects are based on the PLS approach (Conducted in WarpPLS) using Multigroup Analysis (MGA).
References:
Alwin, D. F., and Hauser, R. M. (1975). The decomposition of effects in path. American Sociological Review, 40, 36–47.
Bollen, K. A. (1989). Structural equations with latent variables. New York: Wiley.
Kaplan, D. (2000). Structural equation modeling: foundations and extensions. Thousands Oaks, California: Sage.
Kock, N. (2011). Using WarpPLS in e-Collaboration Studies: Mediating Effects, Control and Second Order Variables, and Algorithm Choices. International Journal of E-Collaboration, 7(3), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.4018/jec.2011070101
Kock, N. (2011). Using WarpPLS in e-Collaboration Studies: Mediating Effects, Control and Second Order Variables, and Algorithm Choices. International Journal of E-Collaboration, 7(3), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.4018/jec.2011070101
Tukey, J. W. (1964). Causation, regression and path analysis. In Statistics and mathematics in biology.New York: Hafner.
Thurstone, L. L. (1931). The theory ofmultiple factors. Ann Arbor, MI: Edwards Brothers.